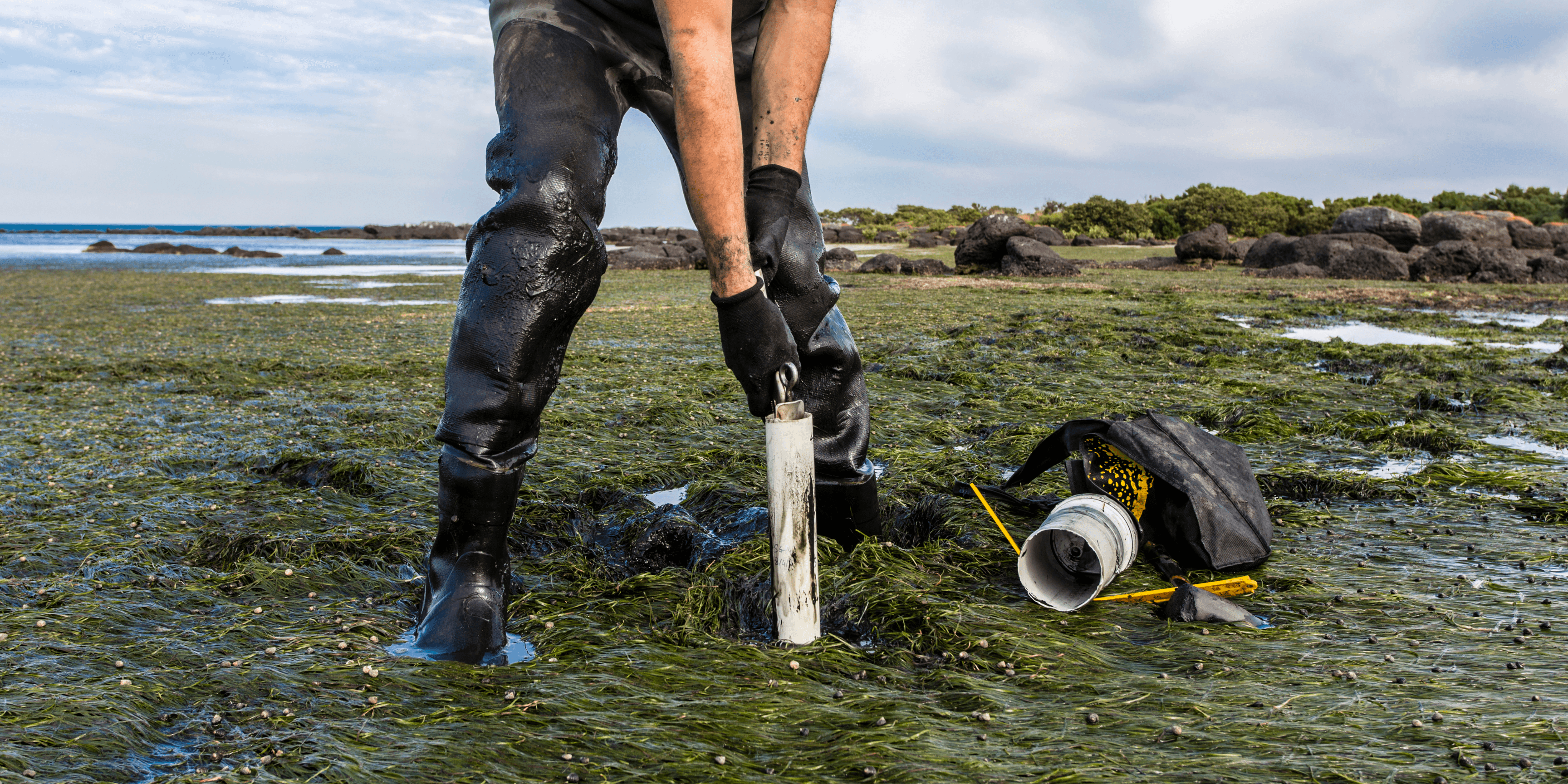

Carbon Sequestration: The Costly Challenge of Capturing and Storing Carbon
In the fight against climate change, carbon sequestration emerges as a crucial tool for reducing greenhouse gas emissions. It involves capturing carbon dioxide (CO2) from industrial processes and power plants, effectively storing it to prevent its release into the atmosphere. While carbon sequestration holds immense promise, it also encounters significant hurdles, predominantly in the form of high costs. This blog post explores the reasons behind the expense of carbon sequestration and sheds light on the challenges surrounding its implementation.
Understanding the Cost Factors of Carbon Sequestration:
When it comes to carbon sequestration, various factors contribute to its high costs. The intricate nature of developing and implementing carbon capture technologies presents a significant challenge. Retrofitting existing industrial facilities and power plants with carbon capture systems incurs substantial expenses, as does conducting research and development to enhance the efficiency and scalability of these technologies.
Moreover, capturing and compressing carbon dioxide demands substantial energy inputs, resulting in increased operational costs. Transporting and injecting the captured CO2 into storage sites, such as geological formations, further escalates energy requirements and associated expenses.
Establishing storage infrastructure, including pipelines and storage sites, requires significant investment. The process of securing suitable geological formations for long-term storage poses its own challenges, thereby adding to the overall expenses incurred during carbon sequestration projects.
Economic Challenges Associated with Carbon Sequestration:
Economic viability plays a vital role in the widespread adoption of carbon sequestration. The high costs associated with carbon sequestration technologies often render it economically unfeasible for many industries and regions. Achieving economies of scale presents a considerable hurdle, impeding cost reduction and the extensive deployment of these technologies.
Uncertainty surrounding carbon pricing mechanisms and policies introduces financial risks for companies investing in carbon sequestration projects. The lack of long-term regulatory frameworks and incentives further dampens private investment, posing a significant barrier to the implementation of carbon sequestration.
Additionally, the prevalence of cheaper and more accessible fossil fuels compared to low-carbon alternatives hampers efforts to incentivize widespread adoption of carbon sequestration.
Environmental and Operational Challenges
Carbon sequestration projects face environmental and operational challenges that amplify their costs. Ensuring the effectiveness and integrity of carbon storage sites demands robust monitoring and verification systems, contributing to operational expenses. Ongoing monitoring and maintenance expenditures are necessary to prevent CO2 leakage and maintain secure storage sites.
Public perception, concerns, and limited awareness about carbon sequestration can hinder its widespread acceptance. Building public support and understanding becomes crucial in developing the necessary policies and funding mechanisms required for large-scale implementation.
The long-term liability of stored CO2 and the potential risks associated with leakage or unintended consequences pose legal and operational challenges. Establishing effective regulatory frameworks is paramount in instilling confidence and mitigating risks in carbon sequestration projects.
Conclusion:
Carbon sequestration holds immense potential in the fight against climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. However, its widespread adoption faces significant challenges, primarily due to the high costs involved. Technological complexities, high energy requirements, storage infrastructure development, economic factors, and environmental and operational challenges contribute to the overall expense of carbon sequestration.
Addressing these challenges necessitates collaborative efforts from governments, industries, researchers, and policymakers. Innovative solutions, incentivized investment, and supportive regulatory frameworks are essential for overcoming these hurdles. By surmounting these challenges, carbon sequestration can play a crucial role in creating a more sustainable future and mitigating the impacts of climate change. Together, we can tackle the costly challenge of carbon sequestration and pave the way for a cleaner, greener world.


Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.